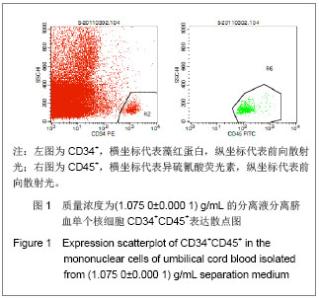
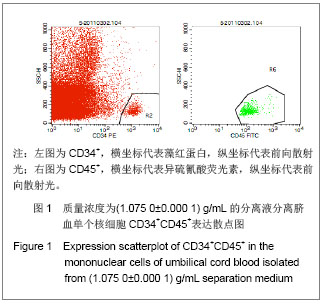
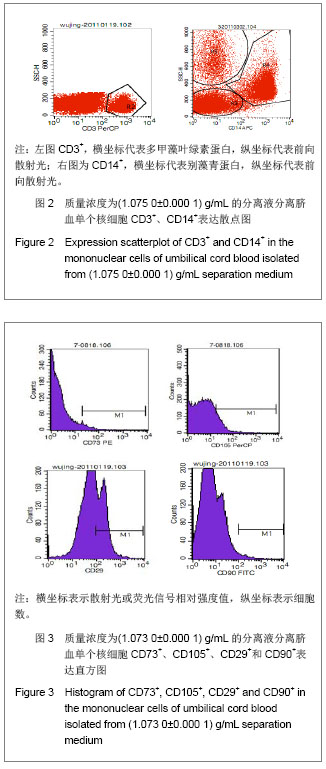
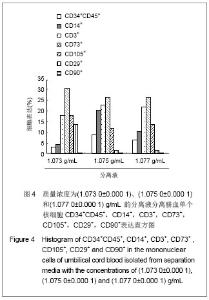
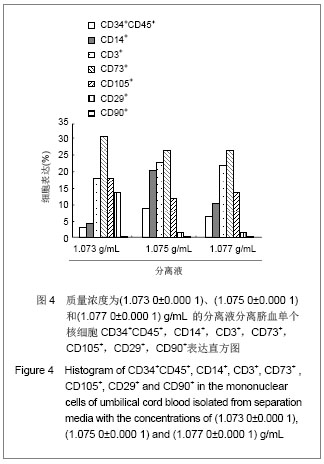
| [1]Spellman S, Hurley CK, Brady C, et al. Guidelines for the development and validation of new potency assays for the evaluation of umbilical cord blood. Cytotherapy. 2010;30(3): 376-378. [2]Yamamoto S, Ikeda H, Toyama D, et al. Quality of long-term cryo- preserved umbilical cord blood units for hematopoietic cell transplantation. Int J Hematol. 2010;93(1):99-105.[3]Prockop DJ, Brenner M, Fibbe WE, et al. Defining the risks of mesenchymal stromal cell therapy. Cytotherapy.2010;12(5): 576-578.[4]Barcelos LS, Duplaa C, Kränkel N, et al. Human CD133+ progenitor cells promote the healing of diabetic ischemic ulcers by paracrine stimulation of angiogenesis and activation of Wnt signaling. Circ Res.2009;104(8): 1095-1102.[5]Tracy ET, Zhang CY, Gentry T, et al. Isolation and expansion of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells from cryopreserved human umbilical cord blood. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(6): 722-729. [6]Zhu ML,Wu XR,Chen RG,et al .Zhongguo Shuxue Zazhi.2002; 15(3):179-180.朱美玲,伍新尧,陈汝光,等.不同分离方法分离脐血造血细胞效率的比较[J].中国输血杂志, 2002,15(3):179-180.[7]Basford C, Forraz N, Habibollah S, et al. Umbilical cord blood processing using Prepacyte-CB increases haematopoietic progenitor cell availability over conventional Hetastarch separation. Cell Prolif. 2009,42(6):751-761. [8]Zhang SH, Lin DD, Zhang MJ, et al. Zhongguo Xuexichongbing Fangzhi Zazhi.2007;19(3):192-195. 张素华,林丹丹,张美娟,等.Ficoll 密度梯度离心法分离猪外周血单个核细胞条件的探讨[J].中国血吸虫病防治杂志,2007,19(3): 192-195. [9]Ma Li, Liu DJ, Li DT, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(38):7401-7406. 马力,刘大军,李德天,等.不同分离方法及培养条件对兔骨髓间充质干细胞生长增殖及生物学特性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(38):7401-7406. [10]Guo JQ,Liu AB,Shen D. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(45):8447-8450.郭继强,刘爱兵,沈丹.两步法分离脐带血单个核细胞的最佳条件[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复杂志,2011,15(45): 8447-8450.[11]Han H, Hanyang APT, Maeul YJ, et al.Method of isolating and culturing mesen- chymal stem cell derived from Umbilical cord blood. U S Patent. US 7704739B2. Apr.27,2010. [12]王怀林.骨髓脐带血干细胞体外分离试剂盒及其应用方法.中国专利,发明,CN101144070,2008.03.[13]Lam GK, Subramanyam L, Orton S, et al. Minimizing red blood cell contamination while isolating mononuclear cells from whole blood: the next step for the treatment of severe hemolytic.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189(4):1012-1016.[14]Rocha V, Sanz G, Gluckman E, et al. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol. 2004;11(6):375-385. [15]Polisetti N, Chaitanya VG, Babu PP, et al. Isolation characterization and differentiation potential of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Neurol India. 2010;58(2):201-208.[16]Boyle AJ, Schulman SP, Hare JM, et al. Stem Cell Therapy for Cardiac Repair Ready for the Next Step. Circulation.2006; 114(25):339-352.[17]Chitteti BR, Liu Y, Srour EF. Srour Genomic and Proteomic Analysis of the Impact of Mitotic Quiescence on the Engraftment of Human CD34+ Cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6(3):e17498.[18]Bourzac C, Smith LC, Vincent P, et al. Isolation of equine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a comparison between three protocols. Equine Vet. 2010; 42(6):519-527. [19]Singh K, Srivastava A, Mathur N, et al. Evaluation of four methods for processing human cord blood and subsequent study of the expansion of progenitor stem cells isolated using the best method. Cytotherapy.2009;11(6):768-777.[20]Phuc PV, Nhung TH, Loan DT, et al. Differentiating of banked human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into insulin-secreting cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(1):54-63.[21]Peters R, Wolf MJ, van den Broek M, et al. Efficient Generation of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood in Stroma-Free Liquid Culture. PLoS One. 2010;5(12):1-14. |